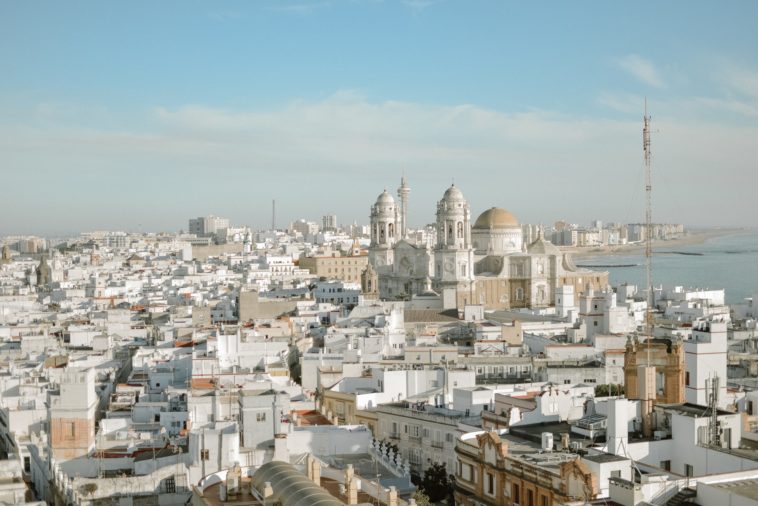
Cádiz is a city and port in southwestern Spain that serves as the capital of the province of Cádiz, one of the eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia. Situated along the coastline, it holds historical, economic, and cultural significance. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the key factors affecting Cádiz, examining the tradeoffs involved in balancing different factors and the challenges associated with different approaches. Furthermore, the importance of considering the impact when making decisions about Cádiz is highlighted.
Geographical Information
| Attribute | Information |
|---|---|
| Longitude | -6.2899 |
| Latitude | 36.5271 |
| Climate | Mediterranean |
| Population | Approx. 120,000 |
| GDP | €3.1 billion (2019) |
| Official Language | Spanish |
| Currency | Euro |
| Religion | Predominantly Catholic |
| Continent | Europe |
Historical Context
Founded by the Phoenicians in 1104 BCE, Cádiz is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe. Its historical significance cannot be understated, given its role as a naval base and a hub for exploration and trade. Understanding its history is crucial for interpreting its current socio-economic landscape and for informed decision-making.
Economy
Trade and Industry
The port of Cádiz has traditionally been the city’s economic lifeline. It serves as a gateway for exports and imports, contributing significantly to the province’s GDP. Industries like shipbuilding and oil refining are also important.
Tradeoffs and Challenges:
- Port Expansion vs Environmental Impact: Expanding the port could lead to increased revenue but might cause environmental degradation.
- Industrialization vs Job Creation: While industries contribute to GDP, they may not create as many local jobs as other sectors, leading to societal imbalance.
Fishing
Fishing has been a traditional occupation but is subject to overfishing and sustainability concerns.
Tradeoffs and Challenges:
- Fishing Quotas vs Livelihoods: Implementing strict fishing quotas safeguards marine biodiversity but impacts livelihoods.
Tourism and Culture
Cultural Heritage
With its historic sites, Cádiz has substantial cultural heritage which attracts tourists.
Tradeoffs and Challenges:
- Tourism vs Cultural Preservation: Heavy tourist traffic can wear down historical sites, requiring a balance between accessibility and conservation.
Festivals
The Carnaval de Cádiz is an iconic cultural event but presents challenges in terms of crowd management and sustainability.
Environment and Sustainability
Coastal Management
Being a coastal city, Cádiz is prone to issues like erosion and rising sea levels.
Tradeoffs and Challenges:
- Coastal Defenses vs Natural Beauty: Building defenses like seawalls can save properties but alter the natural landscape.
Urban Planning
Sustainable urban planning initiatives aim to minimize carbon footprints while ensuring growth.
Tradeoffs and Challenges:
- Development vs Conservation: New construction can fuel the economy but may take a toll on local ecosystems.
Infrastructure
Public Transport
An effective public transport system is essential for reducing emissions and traffic congestion.
Health and Education
Investments in healthcare and education infrastructure are crucial but compete with other sectors for budget allocation.
Governance and Policy Making
Local government has to make decisions based on the tradeoffs between economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability. Different stakeholders have varying levels of influence, requiring a careful balancing act in policy formulation and implementation.
Tradeoffs and Challenges:
- Public Opinion vs Expert Opinion: Policymaking may be influenced by public sentiment, which may not always align with expert recommendations.
Conclusion
Cádiz is a multifaceted city with a rich historical legacy, vibrant economy, and unique challenges. Balancing different factors such as economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability is critical for the city’s future. Comprehensive, data-driven approaches must inform decision-making processes to ensure that the diverse needs and concerns of all stakeholders are addressed, thereby making Cádiz a sustainable, equitable, and economically robust community for generations to come.
By acknowledging the complex tradeoffs and challenges inherent in managing such a diverse city, stakeholders and policymakers can more effectively map out the future of Cádiz, in a manner that honors its past, benefits its present, and secures its future.