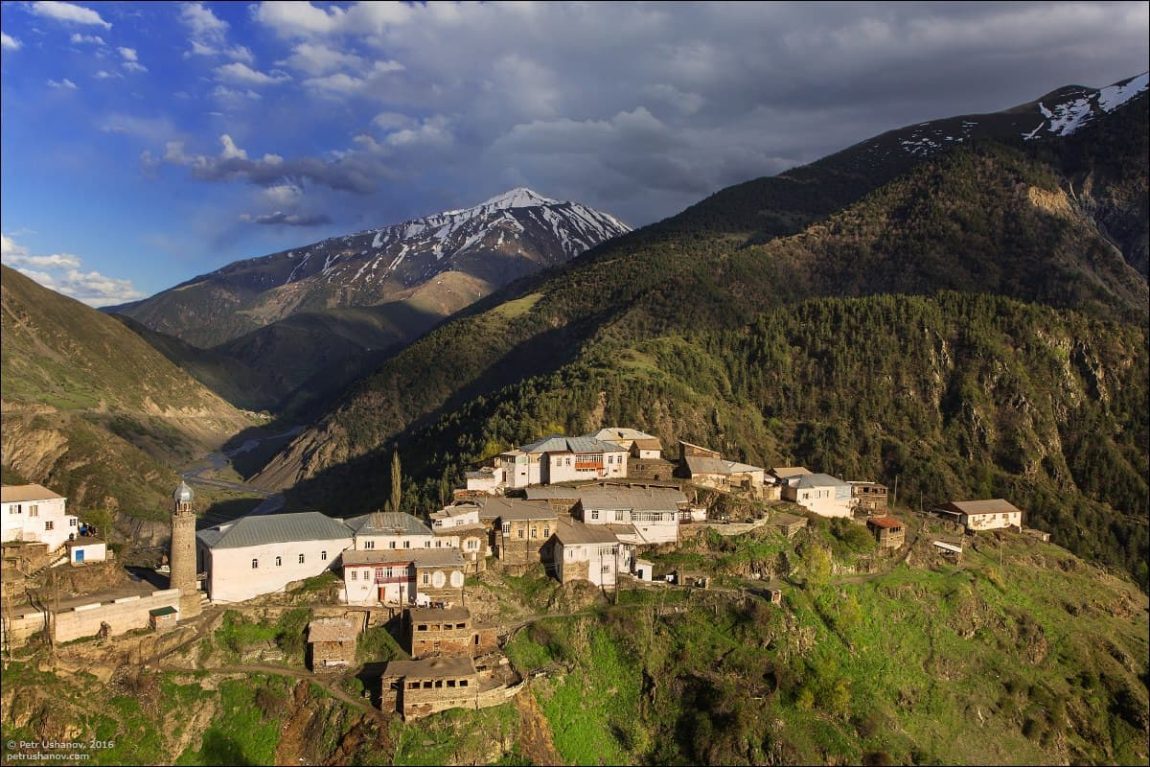
The Caucasus, a remarkable and geopolitically significant region, is nestled at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. This expansive area stretches between the Black Sea to the west and the Caspian Sea to the east, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes, cultures, and historical significance. One of its most iconic features is the mighty Caucasus Mountains, home to Europe’s loftiest peak, Mount Elbrus. In this detailed exploration, we will delve into the political divisions, geographical features, and the rich cultural tapestry that defines this region.
Geographical Overview
Stretching over 1,200 kilometers (746 miles) from the Black Sea in the west to the Caspian Sea in the east, the Caucasus region forms a natural bridge connecting Europe and Asia. Located at approximately 42°N latitude and 45°E longitude, the region occupies a strategic position, influencing both continental and regional dynamics.
Climate
The Caucasus experiences a diverse range of climates due to its vast expanse. To the north, it witnesses a continental climate, characterized by cold winters and warm summers. In contrast, the southern part enjoys a more temperate climate with milder winters and hotter summers. These climatic variations have played a crucial role in shaping the region’s ecology and human settlement patterns.
Physical Geography
The most striking physical feature of the Caucasus is undoubtedly the Caucasus Mountains. These rugged peaks traverse the region from northwest to southeast, forming a natural barrier between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Mount Elbrus, standing proudly at 5,642 meters (18,510 feet) above sea level, is the tallest mountain in Europe and a symbol of natural grandeur.
Political Divisions
The Caucasus is politically divided into northern and southern parts, each with its distinct characteristics and geopolitical significance.
Northern Caucasus
The northern part of the Caucasus is often associated with Russia and comprises the following federal subjects: Adygea, Karachay-Cherkessia, Kabardino-Balkaria, North Ossetia-Alania, Ingushetia, Chechnya, and Dagestan. This region is predominantly Muslim and has a rich cultural heritage. Dagestan, for example, is known for its linguistic diversity, with over 30 languages spoken.
Southern Caucasus
The southern Caucasus includes the independent countries of Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia. This part of the region has witnessed a complex history of political transitions and conflicts. Each country has its own unique language, culture, and religious heritage.
Cultural Diversity
The Caucasus is a melting pot of cultures and traditions, owing to its strategic location as a crossroads for trade and migration. Its population is incredibly diverse, with numerous ethnic groups coexisting and influencing one another. The region is home to various languages, with Georgian, Armenian, and Azerbaijani being the most widely spoken. Additionally, Russian remains a lingua franca in parts of the northern Caucasus.
Religion
Religion also plays a pivotal role in the Caucasus. Islam is the predominant religion in the northern part, while the southern Caucasus has a mix of Christianity (Armenia and Georgia) and Islam (Azerbaijan). These religious affiliations have had a profound impact on the region’s culture, architecture, and way of life.
Economic Significance
The Caucasus region is not only a hub of cultural diversity but also of economic importance.
GDP
The combined GDP of the countries in the region reflects its economic significance. For instance, as of my last knowledge update in September 2021, Russia, which has a significant stake in the northern Caucasus, had a GDP of approximately 1.71 trillion USD. Meanwhile, Azerbaijan’s GDP stood at around 44.57 billion USD, Georgia’s at 17.38 billion USD, and Armenia’s at 13.97 billion USD.
Trade and Energy Resources
The strategic location of the Caucasus has made it a vital trade route throughout history. The region is of particular importance in the transportation of oil and gas from the Caspian Sea to global markets. The Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline, for instance, plays a pivotal role in transporting oil from the Caspian region to the Mediterranean.
Conclusion
In summary, the Caucasus region is a captivating blend of geography, culture, and geopolitics. Its strategic location, diverse landscapes, and rich history make it an area of global significance. From the towering peaks of the Caucasus Mountains to the cultural mosaic of its inhabitants, the Caucasus continues to be a source of fascination and intrigue for scholars, adventurers, and policymakers alike.