Exploring the World of 3D Modeling: Techniques, Applications, and Future Prospects
Key Takeaways
- 3D modeling is an essential process in computer graphics, creating detailed representations of objects in three dimensions.
- Techniques like polygonal modeling, subdivision surface modeling, NURBS, Boolean operations, procedural modeling, and digital sculpting are pivotal in crafting detailed 3D models.
- 3D modeling has diverse applications, from engineering and architecture to entertainment and medical fields.
- Advances in software and techniques, like photogrammetry and 3D printing, continually enhance the potential and accessibility of 3D modeling.
- The future of 3D modeling holds promising advancements in realism, efficiency, and practical applications.
The Art and Science of 3D Modeling
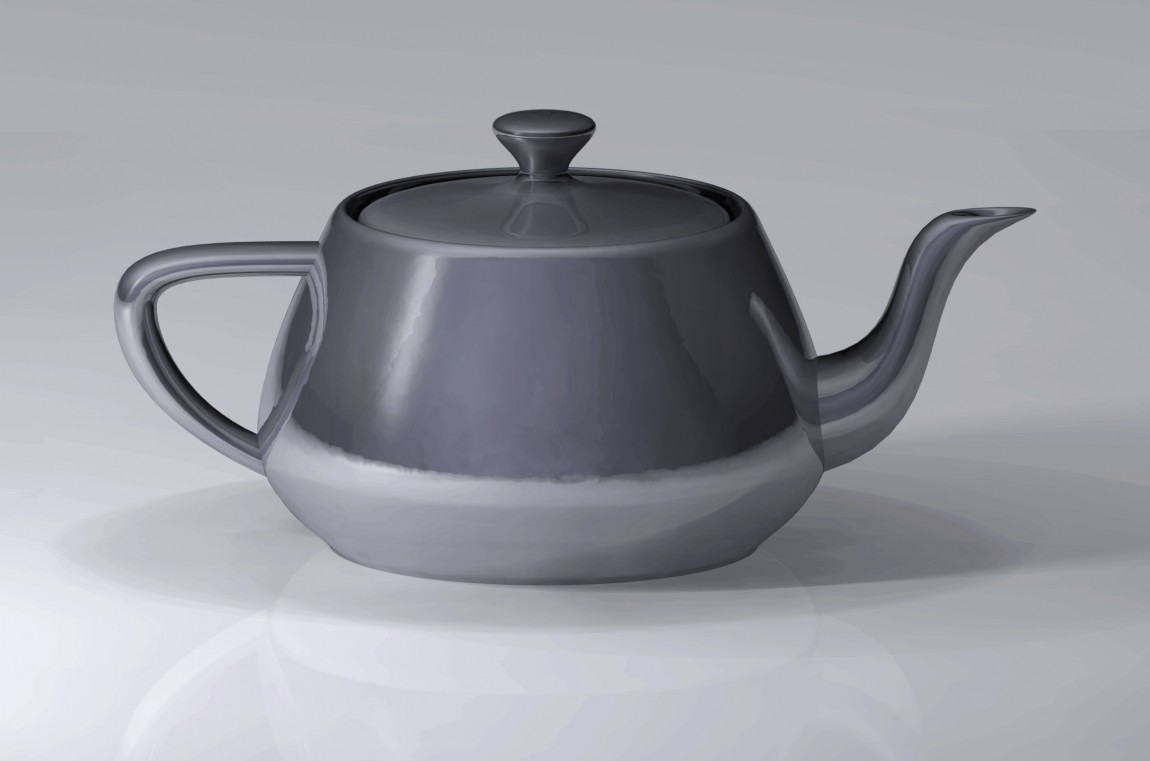
3D modeling stands at the crossroads of art and technology, transforming the way we visualize, design, and interact with digital environments. This dynamic field merges creativity with computational prowess, creating lifelike representations of objects, characters, and scenes. Let’s delve into the techniques that define this vibrant world.
Diverse Techniques for Immaculate Models
- Polygonal Modeling: A foundational technique in 3D modeling, it utilizes vertices, edges, and faces to craft detailed models. It’s particularly adept at creating complex furniture designs with high precision.
- Subdivision Surface Modeling: Ideal for organic shapes, this method smoothens a base mesh to produce high-quality, visually appealing models, crucial for marketing and e-commerce.
- NURBS Modeling: This technique excels in creating smooth, precise surfaces, vital for modeling intricate details in furniture and other design elements.
- Boolean Operations: By combining or subtracting multiple objects, Boolean operations simplify the creation of complex shapes, a staple in architecture and product design.
- Procedural Modeling: This algorithm-based approach automates the creation of detailed models, efficiently generating large-scale environments with a touch of realism.
- Digital Sculpting: A digital counterpart to traditional sculpting, this method allows for detailed, flexible modeling, widely used in film, games, and product design.
Applications Across Industries
3D modeling’s versatility extends to numerous sectors. In the medical field, it provides interactive anatomical representations. The film and gaming industries utilize it for creating characters and environments. Architecture and engineering benefit from accurate, detailed representations of structures and devices. Fashion leverages dynamic 3D clothing models for virtual catalogs and design.
The Future of 3D Modeling
As technology progresses, 3D modeling is poised to reach new heights. We anticipate advancements in realism, efficiency, and integration with emerging technologies like augmented and virtual reality. This evolution will not only enhance existing applications but also unlock new possibilities in design, entertainment, and beyond.
Conclusion
3D modeling, a blend of art and technology, continues to revolutionize various industries. With evolving techniques and applications, it stands as a testament to human creativity and technological advancement, shaping the way we perceive and interact with the digital world. As we move forward, the possibilities in 3D modeling are limited only by our imagination.