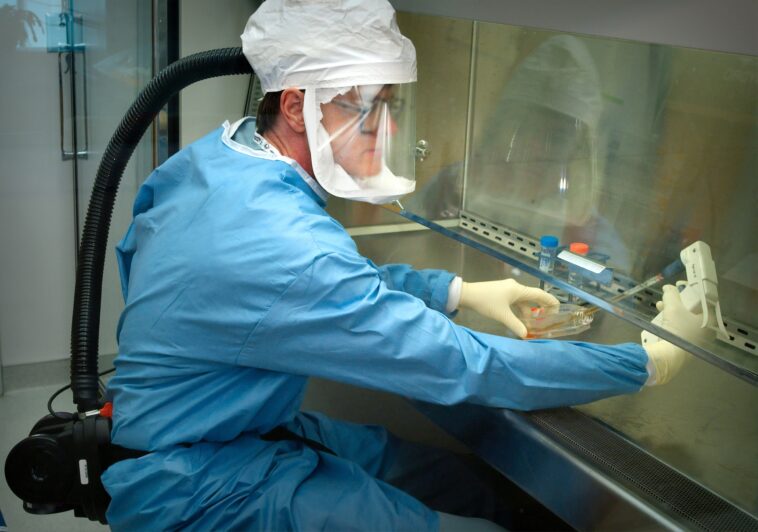
- Biologists’ Focus and Specialization: Biologists study life in various forms, specializing in areas like molecular biology, zoology, or evolutionary biology, with a specific focus on research topics like malaria or cancer.
- Research Methods and Applications: They utilize the scientific method for basic research, contributing to fields like biotechnology and developing medically useful products.
- Education and Training: Biologists typically hold advanced degrees and receive specialized training, contributing to various sectors like academia, private industry, and government.
- Historical Contributions: Pioneers like Darwin, Mendel, and McClintock significantly advanced biological understanding and techniques.
- Diverse Research Areas: Modern biologists engage in a broad range of research, from genetics to ecology, often involving laboratory experiments and fieldwork.
- Biotechnology Impact: Advances in genetics and molecular biology have revolutionized biotechnology, leading to breakthroughs in medicine, agriculture, and environmental remediation.
- Career Variations and Conditions: Biologists work in diverse settings, with some facing unique challenges like fieldwork in varying climates or laboratory safety protocols.
Exploring the World of Biology: A Deep Dive into the Life of Biologists
The Multifaceted Nature of Biological Research
Biologists, as stewards of our understanding of the living world, embark on a quest to unravel the mysteries of life. Their work spans the microscopic, like cells, to the macroscopic, encompassing entire ecosystems. Specialization is key, with biologists delving into subfields such as molecular biology, zoology, or evolutionary biology, each offering unique insights into life’s intricate tapestry.
The Pursuit of Knowledge Through Scientific Method
In their endeavor to expand our knowledge, biologists employ the scientific method. This empirical approach ensures the reliability and validity of their findings. The implications of their research are profound, often contributing to fields like biotechnology. Here, the goal transcends understanding, aiming to develop solutions for human health and wellbeing, like new medical treatments or biotech products.
The Educational Pathway: Shaping Future Biologists
The journey to becoming a biologist typically begins with comprehensive education, encompassing degrees like a bachelor’s, master’s, or doctorate. This academic path is not just about acquiring knowledge; it’s about honing the skill of inquiry and research. It reflects a centuries-old apprenticeship tradition, blending learning with hands-on research under the guidance of experienced mentors.
Historical Landmarks in Biology
The field of biology stands on the shoulders of giants. Figures like Francesco Redi, Charles Darwin, and Barbara McClintock have paved the way for contemporary biological research. Their contributions, ranging from the discovery of the cell to the formulation of evolution theory and genetic principles, have been cornerstones in our understanding of life.
The Diverse Realms of Biological Inquiry
Today’s biologists engage in a spectrum of research activities. Some, like geneticists or neuroscientists, focus on specific aspects of life, such as heredity or the nervous system. Others, like ecologists or evolutionary biologists, explore the broader dynamics of life and its development over time. Their work often requires a blend of laboratory research and field studies, each offering unique insights and challenges.
The Transformative Impact of Biotechnology
One of the most dynamic areas of biology is biotechnology. Here, the knowledge gained from genetics and molecular biology is applied to create innovative solutions, from life-saving drugs to improved agricultural practices. This field stands as a testament to the practical application of biological research, demonstrating its pivotal role in advancing human welfare.
The Working Life of Biologists
Biologists’ work environments are as varied as their research topics. From the tranquility of a laboratory to the unpredictability of fieldwork, their professional lives are a blend of intellectual rigor and practical challenges. They must often balance research demands with the pursuit of funding, all while ensuring their work adheres to ethical and safety standards.
Recognizing Excellence in Biology
The contributions of biologists are often recognized through prestigious awards like the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine or the Crafoord Prize in Biosciences. These honors not only acknowledge individual achievements but also highlight the critical role of biology in advancing human knowledge and welfare.
Acknowledging the Pioneers of Biology
In this magnificent journey through the history of biology, we must pause to honor those who have laid the foundations of our understanding. Francesco Redi, revered as the founder of biology, set the stage for an era of enlightenment in understanding life. Robert Hooke’s coining of the term “cell” marked a pivotal moment, likening the microscopic structures to honeycomb cells and paving the way for cellular biology.
Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace, through their independent formulation of the theory of evolution by natural selection, revolutionized our perception of life’s diversity. Darwin’s seminal work, “On the Origin of Species,” not only proposed the concept of natural selection but also emphasized the gradual divergence of species over time. This theory remains a cornerstone, influencing nearly all aspects of biological study.
Gregor Mendel’s principles of inheritance, formulated in 1866, laid the groundwork for modern genetics, unraveling the mysteries of heredity and genetic variation. The discovery of DNA’s structure by James D. Watson and Francis Crick, building upon the contributions of Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin, marked another monumental advancement, revealing the blueprint of life.
The cloning of a mammal from an adult somatic cell, led by Ian Wilmut and his team in 1996, showcased the incredible potential of genetic research, opening new frontiers in biology.
The Academic Foundation: Educating Future Biologists
The pathway to becoming a biologist is rooted in a robust educational framework. Undergraduate degrees encompass a vast array of disciplines, from molecular and cellular biology to ecology and physiology. This diverse curriculum, enriched with courses in physics, chemistry, and mathematics, equips aspiring biologists with a comprehensive understanding of life’s complexities.
Graduate studies, be it a master’s or a doctorate, offer a deeper dive into biology’s subdisciplines. Here, students engage in advanced research, often under an apprenticeship model, a tradition dating back to the 1800s. This phase of education is crucial, molding students into experts in their chosen field, whether it be genetics, neuroscience, or any of the myriad branches of biology.
The Broad Spectrum of Biological Research
The realm of biological research is vast and varied. Biologists in basic research contribute to our fundamental understanding of life, from the molecular to the ecological level. Their work, often experimental, spans various settings, from the controlled environment of a lab to the unpredictability of natural habitats.
Applied research in biology seeks to utilize the findings of basic research for practical applications. This branch plays a pivotal role in advancements in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental conservation. Biologists in this field often navigate the intersection of science and industry, balancing research goals with commercial implications.
The rise of biotechnology marks a significant evolution in the field. Leveraging genetic and molecular biology knowledge, biologists are now at the forefront of creating innovative solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing challenges.
Specializations within Biology
The diversity within the field of biology is reflected in the array of specializations available. Geneticists, neuroscientists, developmental biologists, biochemists, and molecular biologists, to name a few, each contribute unique perspectives and expertise. This specialization allows for a more profound and nuanced understanding of life in all its forms.
The Life of a Biologist: A Career of Discovery and Challenge
Biologists’ careers are as diverse as their research subjects. While some may find themselves in the predictable routine of a laboratory, others may embark on adventurous fieldwork in varying climates and conditions. Their work schedule can be demanding, often dictated by the nature of their research and the need for funding.
Despite the challenges, a career in biology offers an unparalleled opportunity to explore and understand the living world, contributing significantly to our knowledge and well-being.
Honoring Excellence in Biology
The recognition of excellence in biology is exemplified by prestigious awards like the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and the Crafoord Prize in Biosciences. These accolades not only celebrate individual achievements but also underscore the profound impact of biological research on society and our understanding of life. They serve as a testament to the relentless pursuit of knowledge and the transformative power of scientific discovery in biology.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving World of Biology
In summary, the field of biology is a dynamic and ever-evolving discipline, rich in history and diversity. Biologists, through their dedicated research and exploration, continue to unravel the mysteries of life, contributing profoundly to our understanding of the natural world and its myriad forms. Their work, spanning from the molecular to the ecological, has far-reaching implications, influencing fields like medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
As we continue to face global challenges, the role of biologists becomes increasingly crucial. Their ability to innovate, adapt, and apply their knowledge to real-world problems underscores the significance of biology in shaping a better future for all. The journey of discovery in biology is far from over, and its contributions will undoubtedly continue to inspire and transform the world we live in.