Unveiling the Mystique of Caves: A Journey into Earth’s Hidden Depths
Key Takeaways:
- Caves are fascinating natural structures formed through various geological processes, including chemical reactions and erosion.
- Speleology, the study of caves, offers insights into these underground environments, emphasizing their ecological and archaeological significance.
- The diversity of cave types—from ice caves to volcanic lava tubes—highlights the complexity of their formation.
- Caves are not just scientific curiosities; they hold profound cultural and historical importance, serving as shelters, sacred sites, and canvases for ancient art.
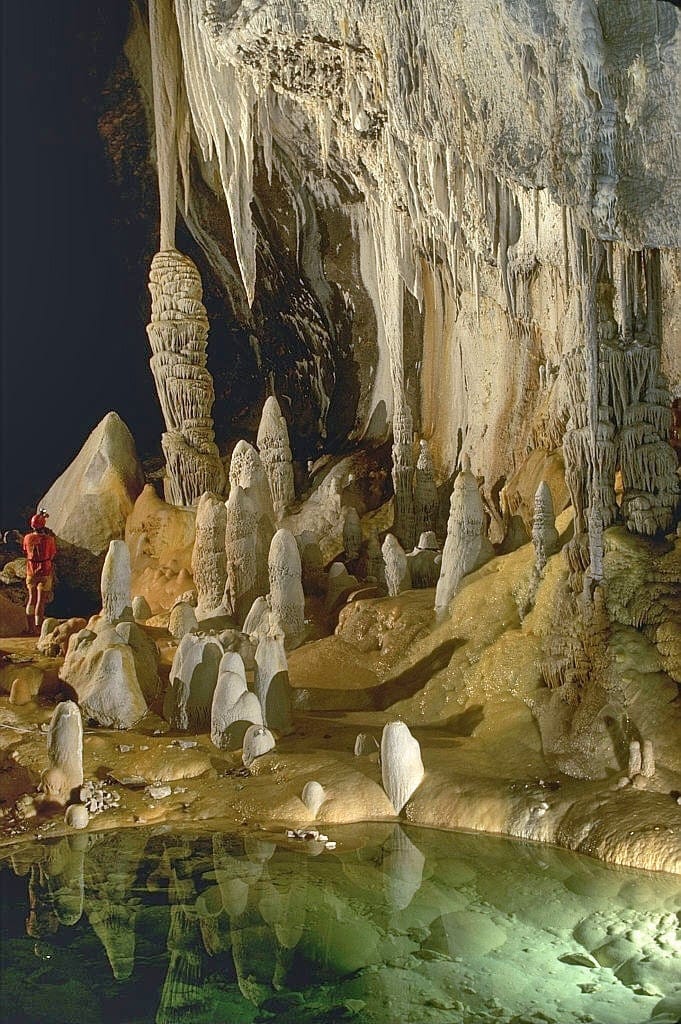
I remember the first time I stepped into a cave. It was a chilly morning, the sky a blanket of gray, as if the earth itself had decided to hide away its secrets beneath. There, at the mouth of a gaping limestone cavern, the air whispered of untold stories, beckoning me into the darkness beyond.
The Enigma of Formation
Caves, those enigmatic voids beneath the earth’s surface, come into being through an intricate dance of nature’s forces. The process, known as speleogenesis, involves everything from water eroding rock to chemical reactions dissolving it away. I’ve wandered through enough caves to realize that each one tells the story of its own creation—be it the slow drip of mineral-rich water forming stalactites or the violent eruptions that carve out lava tubes.
A Spectrum of Wonder
As diverse as the environments above ground, caves vary immensely. Imagine walking through an ice cave beneath a glacier, the air crisp and the frozen sculptures shimmering in the muted light. Contrast that with the oppressive heat of a lava tube, where the earth’s fiery breath still lingers, and the walls are etched with the flow of ancient molten rock.
Life in the Shadows
Delving deeper, caves are more than geological marvels; they are vibrant ecosystems. In the dim light, life thrives in forms most bizarre. From blind fish navigating the perpetual darkness to bats hanging in quiet contemplation, each creature is a testament to life’s adaptability. It’s a humbling experience, standing in a vast chamber, listening to the distant drip of water and the soft flutter of wings—life pulsing in the dark.
Echoes of the Past
Beyond their natural beauty, caves are vaults of human history. They have served as shelters against the elements and canvases for ancient artists, their walls adorned with paintings that reach back to the dawn of human expression. Each mark tells a story—a hunt, a battle, a dance. Caves like Lascaux in France and Altamira in Spain offer us a glimpse into the minds of our ancestors, preserved in the quiet darkness.
The Call of the Unknown
For those who hear it, the call to explore these subterranean realms is irresistible. Caving, or spelunking as it’s known, is not just a pastime; it’s a journey back through time, a plunge into the unknown. Every twisted passage and hidden chamber offers a piece of the puzzle that is our planet’s past, and perhaps, a reflection of ourselves.
As we tread softly on the delicate grounds of these hidden worlds, we’re reminded of our fleeting presence here. Caves are more than just holes in the ground—they are the keepers of secrets, the echo chambers of time. And as we emerge back into the light, the shadows whisper behind us, holding tight to their mysteries.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What causes caves to form?
Caves form through various processes, including chemical reactions that dissolve soluble rocks like limestone, physical erosion by water, or volcanic activity creating lava tubes. - Can caves be found everywhere in the world?
While caves are widespread, their distribution depends on geological conditions. Areas with abundant limestone or volcanic activity are particularly rich in caves. - What are some dangers associated with exploring caves?
Cave exploration can be hazardous due to unstable structures, potential for flooding, and disorientation. Proper equipment and experienced guidance are crucial for safety. - How are caves important to science?
Caves are crucial for studies in geology, biology, and archaeology, offering insights into Earth’s history, unique ecosystems, and human past. - Why are caves significant in history and culture?
Caves have served as natural shelters, religious sites, and canvases for early human art, reflecting their significance across various cultures and eras.