Journey into the Abyss: Discovering the Secrets of the Deep Sea
Key Takeaways:
- Mystical Depths: The deep sea, starting at about 200 meters below the surface, remains one of Earth’s least explored biomes, cloaked in perpetual darkness and subject to immense pressures.
- Unique Inhabitants: Organisms in the deep sea exhibit fascinating adaptations for survival, relying on sources like marine snow for nourishment in an environment devoid of sunlight.
- Human Impact: Despite its remoteness, the deep sea faces threats from human activities, including pollution and deep-sea trawling, which impact its delicate ecosystems.
- Scientific Endeavors: Modern explorations like those by the Trieste, Kaikō, and Nereus have expanded our understanding of these depths, though much remains undiscovered compared to terrestrial and shallower marine environments.
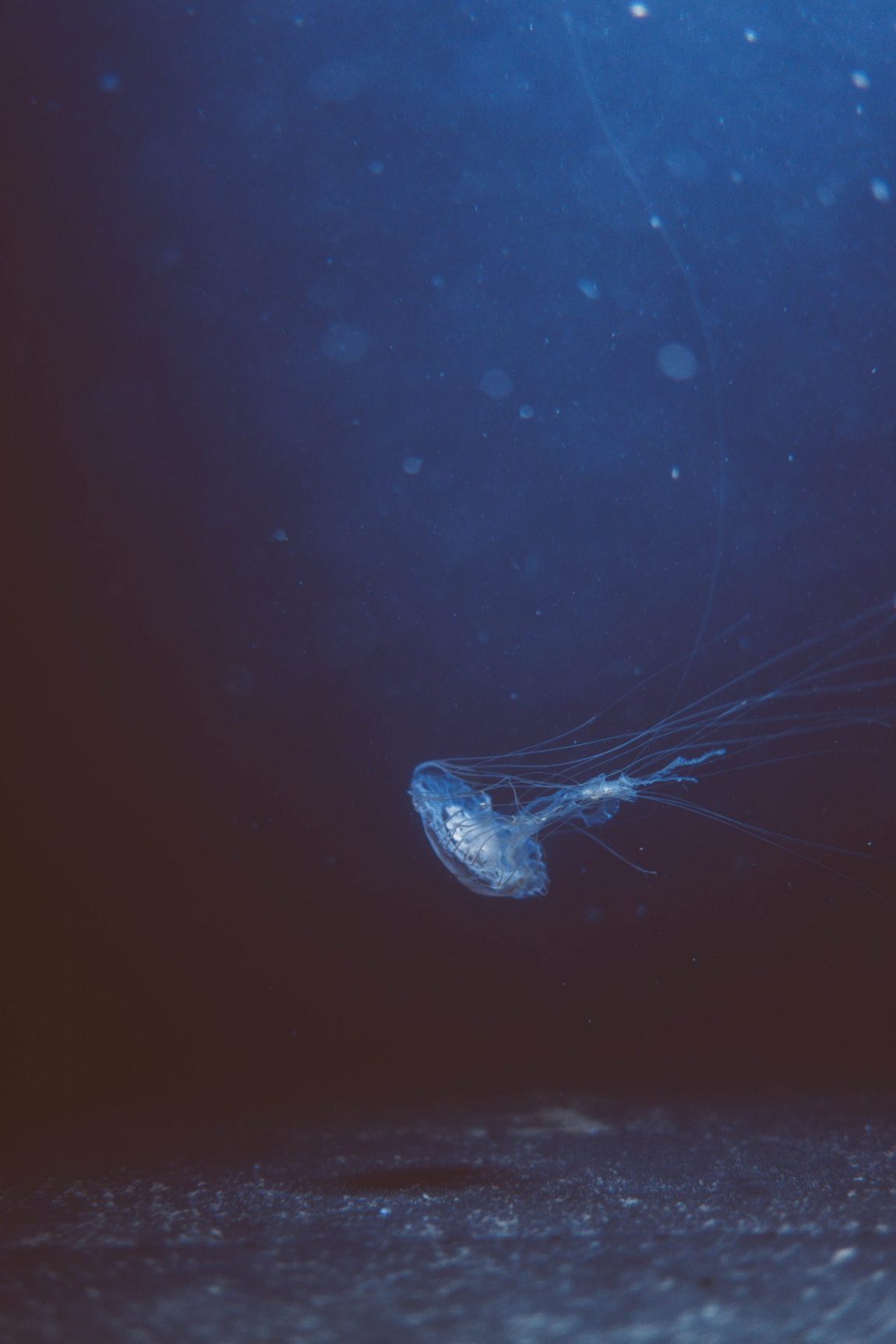
The allure of the deep sea is like a call to the unknown. It beckons with the mystery of an alien world right here on our planet. Beneath the surface waves, the ocean plunges into darkness, a realm where sunlight dares not tread. This is a place of profound mystery and staggering pressure, a canvas for some of nature’s most ingenious adaptations.
A World Beyond the Light
Imagine you’re diving past the sunlit layers of the ocean, descending beyond 200 meters where the last rays of light fade into oblivion. Here, in the perpetual twilight of the mesopelagic zone, life must find a way without the sun’s energy. Creatures here rely on the sparse banquet of marine snow—organic debris that cascades down from the ocean’s productive upper layers. This material supports a bizarre array of life, from giant squid to microscopic organisms, all adapted to the darkness.
The Pressure’s On
As you sink deeper, every 10 meters ratchets the pressure up by another atmosphere. It’s like carrying an increasing stack of weights with each additional step downward. The inhabitants of these depths—some of the most resilient creatures on Earth—have evolved in ways that boggle the mind. Their bodies are often gelatinous and pressure-resistant, avoiding the crushing force that would incapacitate other forms of life.
Unseen Dangers and Hidden Beauty
The deep sea is not just a place of survival against the odds; it’s also a theater of vibrant evolution. Fish with eyes like oversized goggles peer upward, hunting for silhouettes against the faint glow above. Bioluminescent creatures create their own light, staging an underwater ballet of sparks and glows to attract mates or deter predators.
“Isn’t it fascinating how life finds a way, even here?” I often ponder, marveling at the adaptations like bioluminescence that seem more suited to science fiction than our own blue planet.
Human Footprints in Abyssal Plains
Despite its isolation, the deep sea does not escape human influence. Our waste reaches even these remote areas, impacting species that have never seen the light of day. Regulations aim to protect these vulnerable ecosystems, but challenges persist, driven by activities like deep-sea mining and trawling that disrupt the seabed and its inhabitants.
Exploring the Unfathomable
The deep sea is Earth’s final frontier, less known to us than the surface of the moon. Ventures like the Trieste’s descent into the Mariana Trench have provided glimpses into these depths, but much remains unknown. Modern technology now allows us to send unmanned vehicles to these extreme environments, bringing back images and data that slowly piece together the puzzle of the deep ocean.
The journey into the deep sea is a narrative of resilience, mystery, and the indomitable spirit of exploration. It’s a reminder of how much remains unknown on our own planet, waiting in the dark, silent world below the waves.
FAQs About the Deep Sea
- What is the deep sea?
The deep sea generally refers to ocean depths beyond 200 meters where sunlight fails to penetrate, making it inhospitable for photosynthetic life. - How do organisms in the deep sea find food?
Deep sea organisms depend on marine snow, organic material that falls from the ocean’s surface, and other specialized feeding strategies like predation and chemosynthesis. - What are the challenges of exploring the deep sea?
Extreme conditions such as high pressure, low temperatures, and total darkness complicate exploration and research in the deep sea. - How do deep sea creatures adapt to high pressure?
Many deep sea organisms have developed unique physiological and biochemical adaptations, such as pressure-resistant proteins and flexible, gelatinous bodies. - What impact do human activities have on the deep sea?
Pollution, waste dumping, deep-sea mining, and fishing can damage deep sea ecosystems, which are slow to recover due to the conditions and scarcity of resources.