Key Takeaways
- Earthquakes: Nature’s Unpredictable Force – An earthquake is the result of the Earth’s surface shaking due to energy release in the lithosphere, causing seismic waves.
- Tectonic Plates and Fault Lines – Earthquakes primarily occur along tectonic plate boundaries and fault lines, with varying magnitudes.
- Historical Devastation – Notable earthquakes include the 1556 Shaanxi earthquake in China, and the 1960 Chilean earthquake, amongst the most powerful recorded.
- The Science Behind Earthquakes – Understanding earthquakes involves studying seismic waves, fault types, and energy release.
- Human-Induced Earthquakes – Activities such as fracking, mining, and reservoir building can also induce seismic events.
- Measuring Earthquakes – Earthquakes are measured using scales like the Richter scale, moment magnitude scale, and observed effects.
- Global Impact and Preparedness – Earthquakes can cause widespread damage and necessitate comprehensive emergency and preparedness plans.
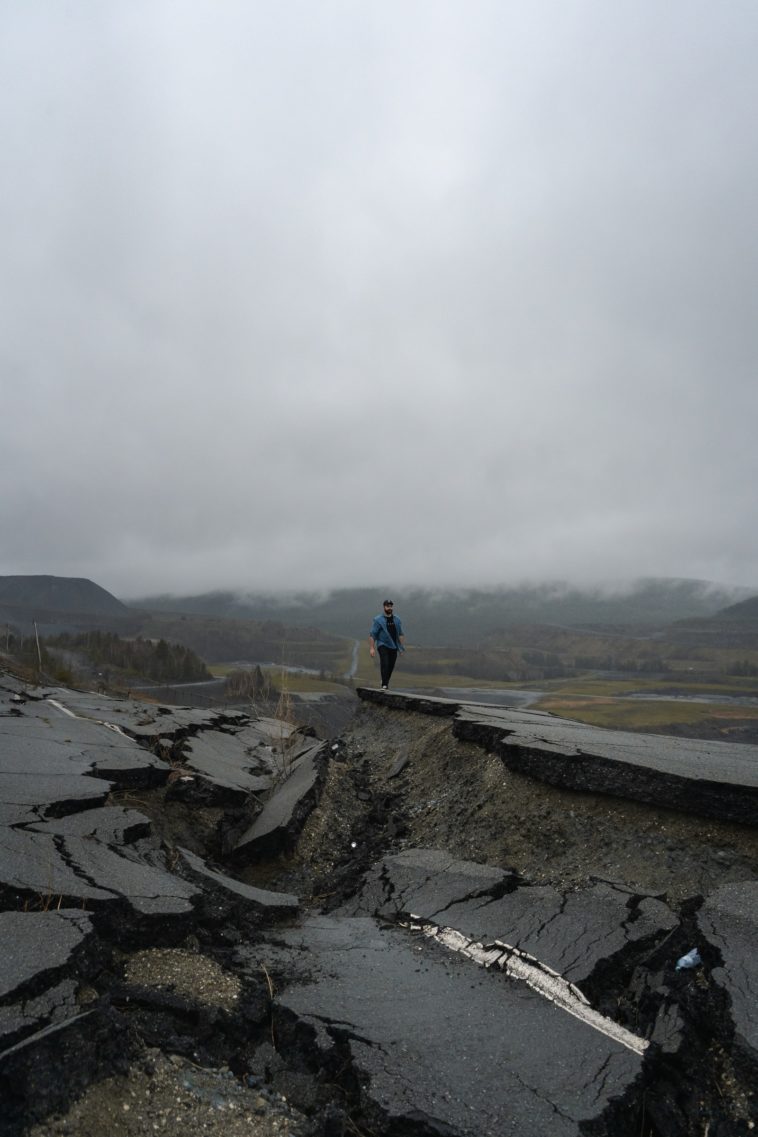
Ah, earthquakes. You know, it’s an incredible force of nature that always leaves a mark, both on the earth and in our hearts. I remember sitting in my living room, feeling the ground shake beneath me. It was a mild tremor, but the sensation of the earth moving was unforgettable. Earthquakes, or as some call them, quakes, tremors, or temblors, are really nature’s way of reminding us of its unpredictable power.
Imagine this: The earth suddenly starts shaking, rattling everything around you. That’s an earthquake for you. It’s like the planet is taking a deep breath, and we’re just along for the ride. These seismic events are caused by the sudden release of energy in the Earth’s lithosphere, creating seismic waves that we feel as shaking.
Here’s something fascinating: most earthquakes occur along tectonic plate boundaries, especially in the Pacific Ring of Fire. It’s like these plates are constantly playing a game of tug-of-war, and when the tension gets too much, the earth shakes.
Let’s dive into a bit of history. The 1556 Shaanxi earthquake in China was one of the most devastating, claiming over 830,000 lives. Can you imagine the magnitude of that disaster? It’s mind-boggling. And then there was the 1960 Chilean earthquake, the largest ever recorded on a seismograph. The power of nature is truly awe-inspiring.
Understanding earthquakes isn’t just about knowing they happen. It’s about diving into the science behind them – the types of seismic waves, the various fault types, and how energy is released during an earthquake. It’s like piecing together a giant puzzle of the earth’s movements.
But here’s a twist: not all earthquakes are natural. Human activities like mining, fracking, and even building large reservoirs can trigger these seismic events. It’s a stark reminder of how our actions can impact the planet.
Measuring earthquakes is a science in itself. The Richter scale, the moment magnitude scale, and even the effects we observe are all ways to quantify these powerful events. It’s like having a thermometer, but for the earth’s shakes and shudders.
Lastly, the impact of earthquakes goes beyond just shaking the ground. They can cause massive destruction, lead to tsunamis, and change landscapes forever. Being prepared for them, understanding the risks, and having a plan can make all the difference. It’s about respecting nature’s power and learning to live with it.
In a way, earthquakes are a reminder of how dynamic and alive our planet is. They’re a natural phenomenon that connects us all, shaking up our world in more ways than one.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What Causes Earthquakes?
Earthquakes are primarily caused by the movement of tectonic plates and the release of energy along faults in the Earth’s crust. - Can We Predict Earthquakes?
Despite advancements in seismology, predicting the exact time and location of an earthquake is still not possible. - What is the Richter Scale?
The Richter Scale is a numerical scale used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake, based on the amplitude of seismic waves. - How Do Earthquakes Cause Tsunamis?
Undersea earthquakes can displace large amounts of water, leading to tsunamis – massive waves that can cause extensive coastal damage. - What Should You Do During an Earthquake?
During an earthquake, it’s important to drop, cover, and hold on. Find a sturdy piece of furniture to take cover under and stay away from windows to protect yourself from broken glass.