Key Takeaways: Unveiling the Mysteries of the Milky Way
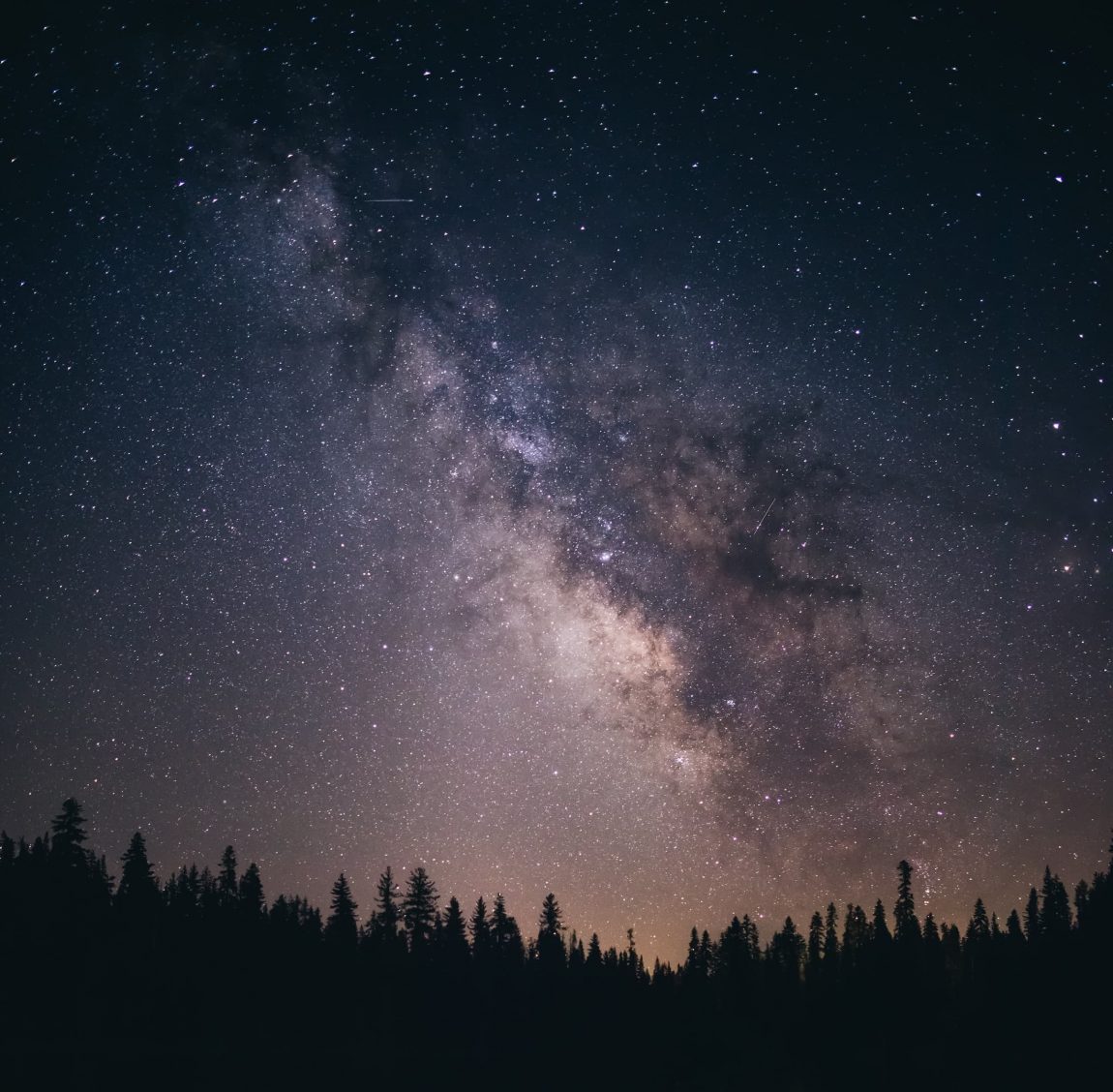
- Galactic Dimensions: Our Milky Way is a majestic barred spiral galaxy, sprawling across 26.8 ± 1.1 kiloparsecs in diameter. It’s not just a collection of stars but a hub of numerous cosmic activities and phenomena.
- Stellar Richness: Home to an estimated 100–400 billion stars, the Milky Way is a stellar metropolis. Each star potentially hosts a retinue of planets, making our galaxy a cradle of countless worlds.
- The Galactic Center: Sagittarius A*, a supermassive black hole, sits at the heart of our galaxy, showcasing the enigmatic and powerful forces at play in the universe.
- Dark Matter Mystery: The Milky Way challenges our understanding of physics with its constant rotational speed, hinting at the invisible yet influential presence of dark matter.
- Interstellar Drama: The Milky Way’s history is marked by celestial events, including mergers with smaller galaxies and interactions that continue to shape its structure.
- A Galactic Dance: The Milky Way, along with its galactic companion, the Andromeda Galaxy, is part of the Local Group, which itself is a fraction of the vast Laniakea Supercluster.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Milky Way
- What exactly is the Milky Way?
The Milky Way is our home galaxy, a massive collection of stars, planets, gas, and dust bound together by gravity. It’s a barred spiral galaxy, part of the Local Group of galaxies. - How many stars are in the Milky Way?
Estimates suggest that the Milky Way contains between 100 and 400 billion stars. This vast number includes a variety of stars, from red dwarfs to massive blue giants. - What’s at the center of the Milky Way?
The center of the Milky Way houses a supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. This black hole has a mass about 4.1 million times that of our Sun. - Can we see the Milky Way with the naked eye?
Yes, under dark skies away from city lights, the Milky Way is visible as a cloudy band stretching across the night sky. This view is actually the combined light of distant stars and other material in our galaxy’s disk. - What is the Milky Way’s future?
Astronomical predictions indicate that in about 4 billion years, the Milky Way will collide with the Andromeda Galaxy. This cosmic event will reshape both galaxies, possibly forming a new elliptical galaxy.
Remember, the Milky Way is more than just a collection of stars; it’s a dynamic and evolving galaxy with a rich history and an intriguing future.