Expanded Paraphrase on World War II
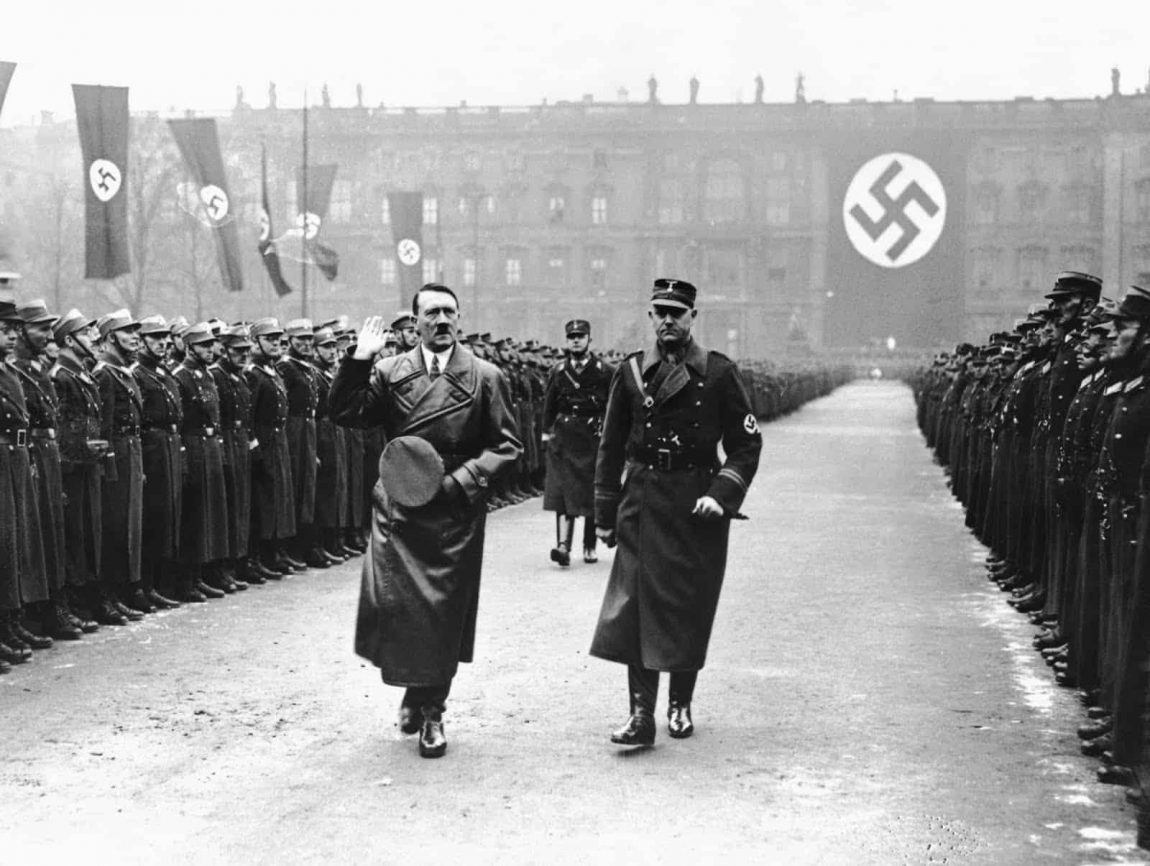
World War II, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2 and also known as the Second World War, stands as one of the most significant global conflicts in history. Spanning from 1939 to 1945, this extensive conflict encompassed the participation of most of the world’s countries, including every major power. These nations split into two primary opposing groups: the Allies and the Axis. This war is notable for being the most comprehensive and widespread conflict in history, involving over 100 million military personnel.
The Prelude to War
The seeds of World War II were sown in the aftermath of World War I. The Treaty of Versailles, which concluded the First World War, imposed harsh penalties and reparations on Germany. This created a climate of resentment and economic hardship, setting the stage for the rise of Adolf Hitler and his Nazi Party. Meanwhile, in Asia, Japan sought to expand its empire, leading to conflicts with neighboring countries, notably China.
Major Participants and Alliances
The Allies primarily consisted of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, the United States, and China. On the other side, the Axis Powers were led by Germany, Italy, and Japan. Over time, numerous other nations joined either side, either through conquests, invasions, or through diplomatic alignments.
Key Events and Battles
World War II was marked by numerous significant battles and events:
- Invasion of Poland (1939): This invasion by Germany is commonly regarded as the event that sparked the war.
- Battle of Britain (1940): A significant air campaign waged by the German Air Force against the United Kingdom.
- Operation Barbarossa (1941): Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union, which eventually turned the tide against the Axis Powers.
- Pearl Harbor (1941): Japan’s surprise attack on the US naval base at Pearl Harbor led to the United States entering the war.
- D-Day (1944): The Allied invasion of Normandy marked the beginning of the end for Nazi Germany.
The Holocaust
A tragic and significant aspect of World War II was the Holocaust, where six million Jews were systematically exterminated by the Nazis. In addition to Jews, other groups such as Romani people, disabled individuals, and political dissidents were also targeted.
Technological and Military Innovations
World War II saw significant advancements in military technology. This included the development of radar, jet engines, and significant improvements in tanks and firearms. The war also witnessed the first use of nuclear weapons when the United States dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
The Aftermath
The war concluded with the unconditional surrender of the Axis Powers. The aftermath of the war saw the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers and the beginning of the Cold War. The United Nations was established to foster international cooperation and prevent future conflicts. The political and geographic landscape of Europe and Asia underwent significant changes.
Legacy
World War II profoundly influenced world politics, economics, and society. It led to the decolonization of Africa and Asia and laid the groundwork for the European Union. The war’s legacy continues to impact global affairs and international relations.
Conclusion
World War II, a colossal conflict that reshaped the world, remains a defining moment in modern history. It altered the course of nations, redrew world maps, and forever changed the global order. Its lessons and legacies continue to be relevant in today’s world.
Key Takeaways:
- World War II was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945.
- It involved most world nations, divided into the Allies and the Axis.
- The war led to significant technological advancements and marked a turning point in modern history.