The overwhelming feeling of helplessness or sadness are common symptoms of depression. While some people think that you can “break out” of depression, it rarely happens. Depression is a typical psychological health problem where people lose interest in things, experience fatigue, and usually have trouble managing their feelings. Psychologists can help you discover the resource of depression usually the first step for feeling much better, along with helping with negative thoughts. Do you observe troubling signs on your own or in a loved one that may indicate the start of depression? You can find out more about psychologists, and different types of psychiatry, at BetterHelp.com.
Symptoms of depression
The main symptoms of depression are a low mood and a sense of sadness, with which the disease often begins. There is also a gradual reduction in daily activities. It is often difficult for patients to get out of bed in the morning or go to work. They no longer enjoy their hobbies and activities, which they used to like.
Their ability to experience satisfaction and pleasure is diminished until they completely lose it, i.e., anhedonia. The sick person feels helplessness and emptiness. In most cases, such moods are more intense in the morning. Depression is primarily identified with a depressed mood, but it is complicated for a person suffering from it to control their emotions – it can be impulsive, irritable, or explosive.
People suffering from depression lose their interest in life and have problems with planning the future. They are often accompanied by a desire for death and suicidal thoughts, which may turn into actions in more severe forms.
Patients with depression experience sleep disorders, especially problems with falling asleep and insomnia, light sleep, and numerous awakenings – especially in the morning. Resting does not bring relaxation, hence fatigue, tearfulness, problems with concentration, and increased sleepiness during the day.

Types of depression:
Depression can be a reaction to traumatic events or appear out of nowhere for no apparent reason. In some patients, symptoms related to low mood, sadness, and lack of motivation to act are predominant. In others, depression manifests itself as insomnia, a lack of morning energy, and appetite. These differences may be due to the type of depressive disorder. The most common are:
Exogenous depression
Exogenous depression, or reactive depression, is a disorder resulting from difficult, traumatic experiences. Reactive depression can cause a loved one’s death, loss of job or health, or chronic stress. Of course, difficult experiences leave their mark on everyone. Most people mourn the loss of loved ones or suffer after the end of the relationship. Endogenous depression is more than just the natural sadness of such situations.
It is a persistent depression that can lead to closing in on yourself, avoiding contact with people, eating disorders, using stimulants, or thoughts of suicide.

Endogenous depression
The causes of endogenous depression are believed to be disturbed biochemistry of the brain, endocrine, or nervous system. This type of depression appears suddenly. It is not associated with any problematic experiences. Often endogenous depression is masked by other ailments, such as headaches, joint pain, cardiac arrhythmia, indigestion, etc. Disturbed circadian rhythms can identify endogenous depression.
Patients often complain of insomnia at night – difficulty falling asleep or waking up very early in the morning. The worst is in the morning. Patients do not have the strength to get out of bed, get dressed, eat breakfast. They feel best in the afternoons and evenings. Endogenous depression is a chronic disease.
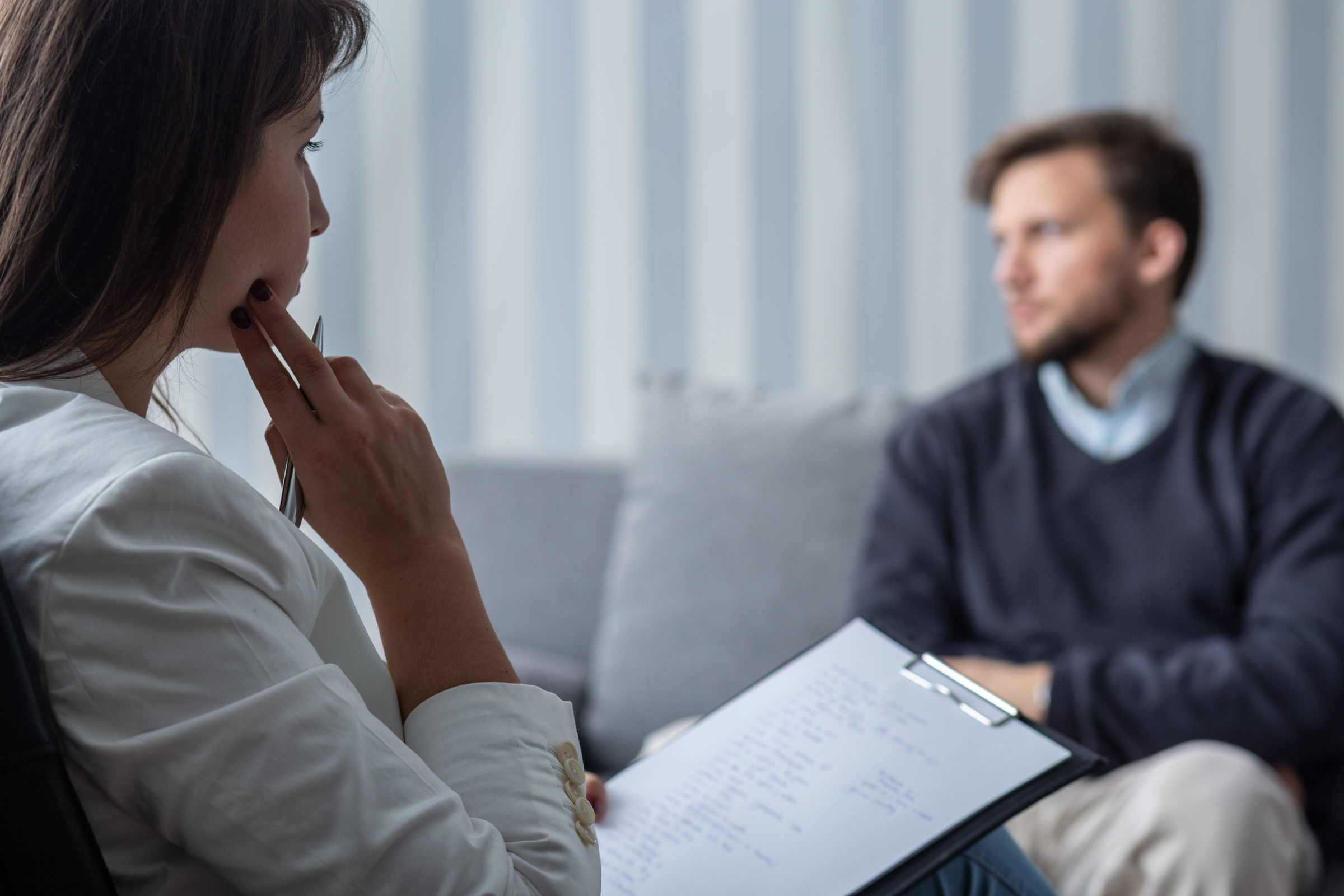

Depression in the course of bipolar disorder
Alternating episodes of depression and mania characterize bipolar disorder. A manic episode appears first, with a short duration followed by a depressive episode, usually much longer.
Depression in bipolar disorder is similar to severe exogenous depression. It requires taking medications and possibly working with a psychotherapist.
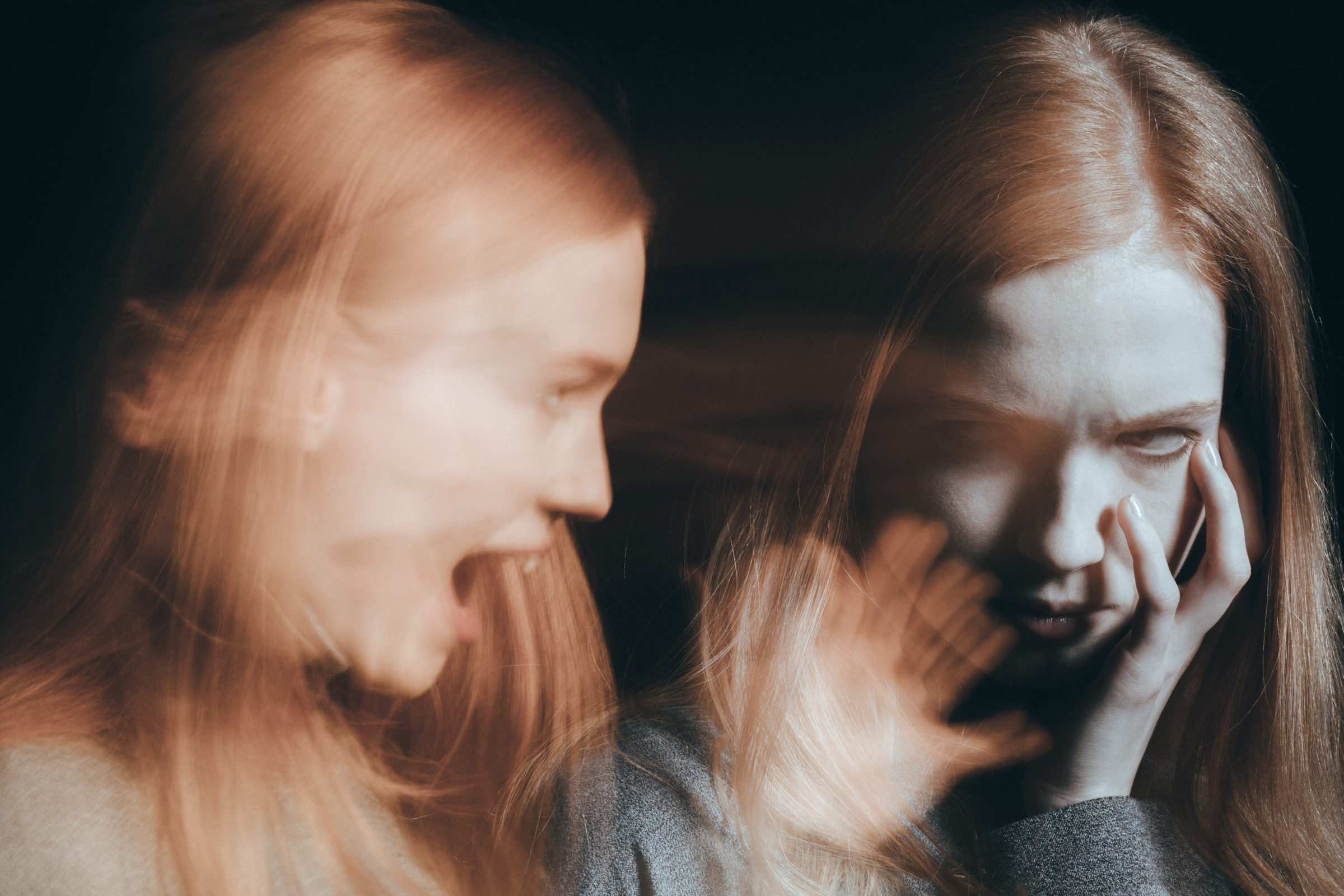

Postpartum depression
Postnatal depression is a mental disorder that can develop up to a year after having a baby. Women often undergo the so-called baby blues, a state of moderate depression caused by intense hormonal changes in a woman’s body after pregnancy. It happens that baby blues stretches and transforms into postpartum depression with its characteristic symptoms: avoidance of contact with the environment, oversensitivity to the child, increased concerns about its health and development, low tolerance for any changes in the circadian rhythm, clinging to certain educated rituals in caring for a child, enormous exhaustion with an inability to rest.
It also happens that postpartum depression does not develop until several months after giving birth, during which the woman functioned without any problems. Treatment of postpartum depression is brutal because young mothers are usually very ashamed of this condition, blaming themselves for being a lousy parent, failing to cope with the role that should be natural for them. In diagnosing and treating postpartum depression, it is very important to be surrounded by a young mother who will mentally support her and help her physically take care of her baby.

Seasonal depression
Seasonal depression is probably the result of insufficient exposure to solar radiation. In this disorder, depression appears cyclically in autumn and winter and disappears in spring and summer. Patients complain of hopelessness, apathy, excessive sleepiness, and increased appetite. They may also experience irritability, difficulty concentrating, loss of interest in daily activities, and reduced libido. Some people explore nutritional support as part of their management plan – https://kizerpharmacy.com/blog/supplements-for-seasonal-depression/ offers a helpful overview of supplements that may provide relief. Taking proactive steps – such as exploring treatment options and lifestyle adjustment – can make a meaningful difference in managing symptoms.

If you recognize any of the symptoms in yourself or a loved one, you should contact a specialist in your area as soon as possible. Any doctor can make an initial diagnosis or suspicion of depression, but qualified psychiatrists can confirm the diagnosis. Depression is an out-of-the-box disease, and it is not easy to recognize depression in yourself, someone, and especially your child.
Delta 8 THC and CBD oil for anxiety
Delta 8 THC has become a hot commodity in the cannabis market and is seen as slightly less psychoactive than traditional marijuana. But, with all of this hype around delta products, finding high-quality tinctures can be tricky. There are even more factors to consider when it comes to determining quality levels for these types of tinctures just like CBD oil; here are a couple of suggestions to get you started! If you want your search done fast, Observer.com made an informed top 3 list for 2021 that will have something perfect no matter what you need from Delta 8 Tincture brands (so don’t wait!).
CBD oil is a chemical compound derived from the cannabis plant. It’s not known definitively how it combats anxiety, but researchers have shown that CBD interacts with your brain in ways that may alter serotonin signals. Researchers believe that CBD oil might work by interacting with a receptor in the brain called CB1, which is related to serotonin. Studies show that this can be an effective treatment for generalized anxiety disorder and various other types of anxiety as well – including:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Social anxiety disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Researchers at Brown University found evidence suggesting that people who use CBD may experience an increase in certain regions within their brains associated with mood regulation, supporting its anti-anxiety effects (study). People suffering from PTSD also saw reduced levels of depression symptoms after taking just one dose; as well as increases in sleep quality and less hyperarousal throughout treatment—all facets crucial for healthy mental functioning.