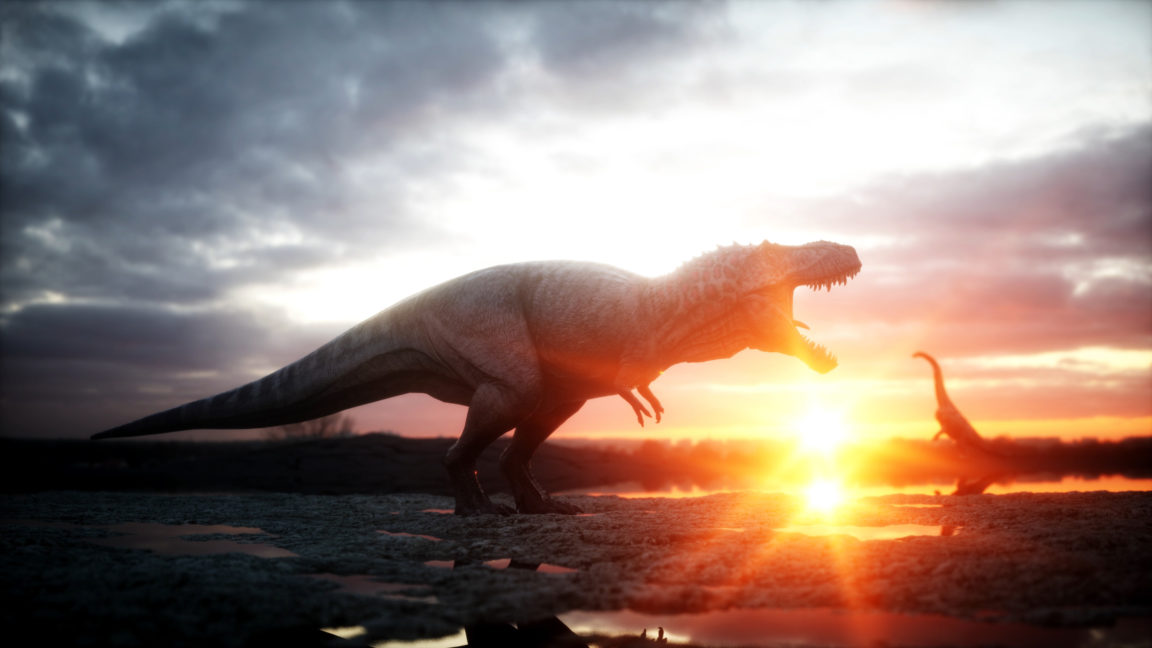
Dinosaurs once conquered the world and were free to roam. These apex predators have fascinated many people for years, especially those interested in learning more about our ancient predecessors. These carnivorous dinosaurs reigned supreme at the top of the food chain, hunting smaller animals and defending their territories to death.
From their appearance to their speed, location and jaw strength, this list takes a look at the top meat-eating dinosaurs that ruled the Triassic period.
Therapods
Therapod dinosaurs were a group of bipedal saurischian dinosaurs that included the largest terrestrial carnivores ever. Therapod dinosaurs are three-toed bipedal dinosaurs that could reach speeds of 27.7 miles an hour and were expert hunters. After examining footprints discovered in La Rioja, Spain, experts believe that these dinosaurs had to evolve quickly so that they could capture their prey easily.
Many carnivorous dinosaurs during the Triassic period can be classified as therapods, such as the next pick, the Herrerasaurus. You can learn more about the mighty therapods by visiting relevant sites and reading some books on the subject.
Herrerasaurus
The Herrerasaurus dinosaur was a type of therapod dinosaur from Southern America. It was also known as one of the earliest dinosaurs and was discovered by the Ischigualasto Formation. It’s named Herrerasuarus after the rancher who discovered it. It loosely translates to ‘Herrera’s lizard” and the dinosaur was medium in size and was a stocky but powerful carnivore. It possessed large teeth that curved inwards which made it very flexible to handle its prey.
These dinosaurs, while hunting, would lock small prey in their powerful jaws and then use powerful, quick body momentum that rendered their prey unconscious. They also hunted small to medium plant-eating dinosaurs and would use their powerful hind legs and their three recurved claws to grasp and rake prey.
Coelophysis
This dinosaur was a small pre-historic pack-hunting dinosaur and was among the first dinosaurs to evolve. It existed during the late Triassic period and was a pack hunter that would hunt in packs of up to eight. These packs would use flanking tactics to surround their prey, giving it no chance to escape. The Coelophysis was relatively small, bipedal and was a therapod dinosaur type that could grow up to three meters.
It had a long narrow head that gave it a stereoscopic vision, giving it a fantastic depth of perception, which added to the qualities that made it a very skilled hunter. Coelophysis could bring down larger animals by slashing bites out of their legs or sides so that they had nowhere to run.

Tawa
Tawa hallae is suspected to have had feathers and could grow to sizes described as that of a large dog. This dinosaur also had a long neck and tail and had a slender snout. Its teeth were sharp and curved, and these were used for hunting its prey. Paleontologists discovered Tawa bones while excavating at the Hayden Quarry in northern New Mexico. The Tawa dinosaur is also suspected to have been the ancestor to the T-rex, this is probably because of the similar build in body with the short arms and long legs.
Its prey included smaller animals, insects as well as carrion and like the coelophysoids, it had a kink in its jaw that allowed it to handle prey better, especially in situations when the prey was trying to escape.
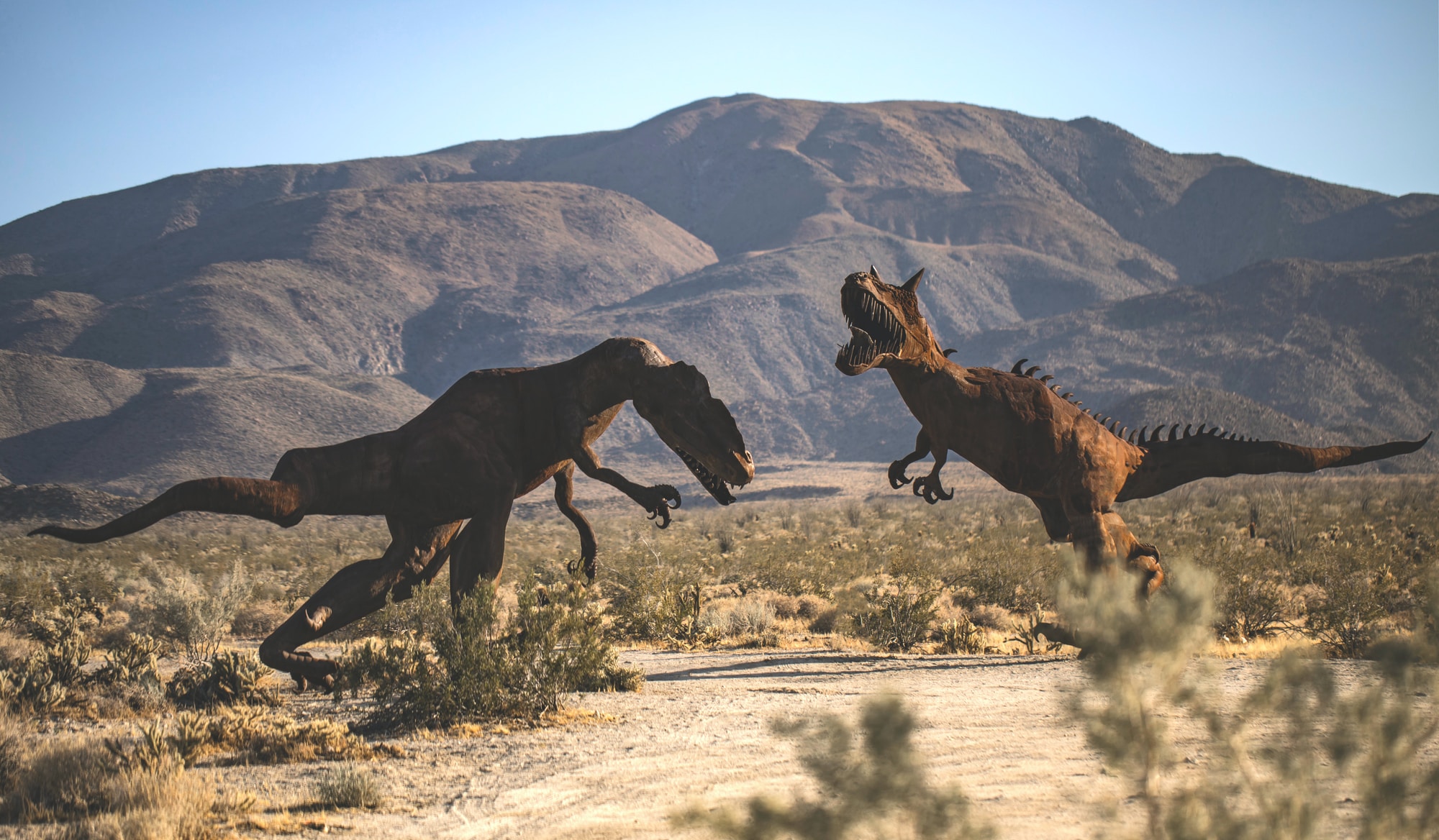

Postosuchus
Postosuchus means “crocodile from post” and this dinosaur lived in the regions that is now Northern America. It could grow to lengths six meters long and heights of up to two meters high. It was good at ambushing its prey and would hunt very well in a herd. They fed on smaller animals and were fiercely territorial creatures and would always be ready to fight to the death if other creatures came into their territory.
Appearance-wise, this dinosaur does look like a crocodile. This species did die out during the end of the Triassic period and was a bipedal dinosaur that could walk on two legs.
Conclusion
The Triassic period lasted for almost 50.6 million years after the Permian period. The Triassic period is one of the shortest periods in the Mesozoic Era and was full of skilled hunting dinosaurs that varied in size, colors and speeds. These pre-historic hunters would flank their prey or ambush them when they least expected it and had kinks in their mouths that secured the prey in their mouth to prevent escape. Fossils of these pre-historic dinosaurs are still being discovered today, and there is still so much for us to know about them.